When newcomers first encounter 2-Aminoterephthalic acid, it may look like just another aromatic compound on a specification sheet. In practice, however, it is a highly versatile chemical intermediate that plays a critical role in modern materials science and chemical synthesis.
Chemically, 2-Aminoterephthalic acid is an aromatic dicarboxylic acid with an amino group attached to the benzene ring. This specific molecular structure gives it a unique dual functionality: it can participate in condensation reactions through its carboxyl groups while also engaging in derivatization or coordination chemistry through its amino group. From my experience working with research labs and industrial customers, this combination is exactly what makes the compound so valuable.
For beginners, the easiest way to understand 2-Aminoterephthalic acid is to view it as a reactive building block—one that chemists rely on to create more complex, higher-value compounds used in advanced applications.
Properties of 2-Aminoterephthalic Acid
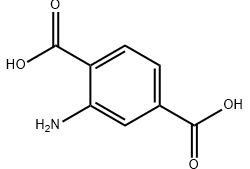
Understanding the properties of 2-Aminoterephthalic acid is essential before working with it. In real-world use, these properties directly influence reaction design, processing conditions, and product performance.
2-Aminoterephthalic acid typically appears as a solid powder, offering good stability under standard storage conditions. Its aromatic backbone contributes to thermal and chemical stability, while the amino group introduces enhanced reactivity compared with unsubstituted terephthalic acid. This balance between stability and functionality is something I have repeatedly seen customers appreciate, especially in research and pilot-scale production.
Solubility behavior is another key point. While it is not highly soluble in water, it shows better compatibility with polar organic solvents, which makes it easier to integrate into controlled synthesis routes. The compound also demonstrates consistent purity and predictable behavior when sourced from a reliable supplier—something beginners should never overlook.
Applications of 2-Aminoterephthalic Acid
The applications of 2-Aminoterephthalic acid are broader than many newcomers expect. Over the years, I have seen it used across multiple fields, particularly where precision chemistry and structural control are required.
One of its most well-known uses is in materials research, especially in the synthesis of functional polymers and advanced frameworks. It is also widely employed in pharmaceutical and fine chemical development, where its structure allows chemists to introduce both rigidity and functionality into target molecules.
In academic and industrial laboratories, 2-Aminoterephthalic acid is frequently selected for custom synthesis projects, because it allows researchers to modify molecular properties without starting from scratch. This flexibility saves time, reduces development costs, and improves experimental reproducibility—key advantages for both beginners and experienced chemists.
Why 2-Aminoterephthalic Acid Is an Important Intermediate
From an industry perspective, 2-Aminoterephthalic acid is important not because of what it is, but because of what it enables. As an intermediate, it serves as a bridge between simple raw materials and sophisticated end products.
In my experience, intermediates that offer both structural rigidity and chemical versatility are always in demand. The amino and carboxyl functional groups allow for multiple reaction pathways, giving chemists freedom in molecular design. This makes 2-Aminoterephthalic acid especially valuable in scalable synthesis, where predictability and yield matter just as much as creativity.
For beginners, this is an important concept: choosing the right intermediate often determines whether a project progresses smoothly or becomes unnecessarily complex. 2-Aminoterephthalic acid consistently proves to be a reliable, adaptable choice.
Choosing High-Quality 2-Aminoterephthalic Acid
Selecting high-quality 2-Aminoterephthalic acid is critical, particularly for those new to chemical sourcing. From years of working with customers, I can say with confidence that quality issues usually arise not from the chemistry itself, but from inconsistent raw materials.
Beginners should pay close attention to purity levels, batch consistency, and supplier reliability. A reputable supplier will provide clear specifications, stable quality control, and technical support when needed. High-purity material ensures cleaner reactions, fewer side products, and better reproducibility—factors that significantly reduce troubleshooting time.
In practice, investing in reliable 2-Aminoterephthalic acid at the start often saves far more time and cost down the line. This is one of the most important lessons I share with new researchers and buyers alike.



