Physical Appearance and Form
2-Bromo-4-chloro-3-fluoro-1-methyl-benzene is a crystalline solid at room temperature, often appearing as a white to off-white powder. Its compact form and fine particle size make it convenient to measure and incorporate into laboratory or industrial processes. Beginners often find its distinct powdery texture helpful for distinguishing it from similar halogenated benzene derivatives. The chemical is typically supplied in sealed, moisture-resistant packaging to maintain quality and prevent contamination during transport or storage.
Molecular Structure and Functional Groups
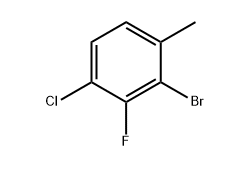
The molecule features a substituted benzene ring with a bromine atom at the 2-position, a chlorine atom at the 4-position, a fluorine at the 3-position, and a methyl group at the 1-position. This combination of halogens and a methyl group results in unique electronic and steric effects, influencing both reactivity and stability. From my experience in working with multi-halogenated benzenes, this specific arrangement makes it a versatile intermediate for a range of organic transformations. Chemists often rely on its structure to modulate reaction pathways in halogen exchange, cross-coupling, and substitution reactions.
Chemical Reactivity and Stability
The presence of multiple halogen atoms introduces controlled reactivity, making 2-Bromo-4-chloro-3-fluoro-1-methyl-benzene suitable for selective substitution reactions. The molecule demonstrates excellent thermal and chemical stability, allowing it to withstand standard laboratory conditions without significant decomposition. Its solubility profile—moderately soluble in polar organic solvents—enables precise reaction control, which is especially important in medicinal chemistry and fine chemical synthesis. In practical applications, understanding the balance between reactivity and stability ensures predictable yields and minimal side reactions, a lesson I’ve repeatedly observed is critical for both new and experienced chemists.
Applications as a Chemical Intermediate
This halogenated benzene derivative serves as a key intermediate in the synthesis of pharmaceutical compounds, agrochemicals, and advanced materials. Its unique combination of bromine, chlorine, and fluorine allows chemists to perform targeted cross-coupling reactions, facilitating the creation of complex molecules efficiently. In research and pilot-scale production, it is commonly used to construct functionalized aromatic systems, contributing to innovations in drug discovery and material science. Beginners often underestimate its value; however, selecting this intermediate can streamline synthesis routes and improve overall product quality, making it a go-to choice in many laboratories.
Handling, Storage, and Quality Considerations
Proper handling of 2-Bromo-4-chloro-3-fluoro-1-methyl-benzene is essential for safety and performance. The compound should be stored in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture. Using gloves, eye protection, and proper ventilation during handling reduces exposure risks. For consistent results, always source material from reliable suppliers, ensuring high purity and batch-to-batch consistency. Over the years, I’ve found that investing in quality material from trusted sources not only reduces experimental failures but also improves reproducibility—a crucial factor for both R&D and industrial applications.



