What is 2-Chloro-4-(2,2-dimethylpropyl)pyridine?
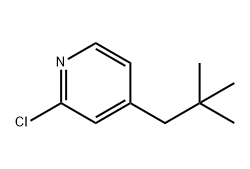
2-Chloro-4-(2,2-dimethylpropyl)pyridine is a pyridine-based chemical intermediate featuring a chloro-substituted aromatic ring and a branched alkyl side chain. This structure provides the compound with good stability and predictable reactivity, making it useful in multi-step synthesis processes across different industrial sectors.
It is commonly supplied in high-purity grades and is frequently used as a building block for more complex molecules, especially where pyridine derivatives play a functional role.
Its compatibility with various organic solvents and reagents gives it versatility, allowing manufacturers to integrate it easily into existing synthesis routes without requiring major process adjustments.
It Matters in Chemical Manufacturing
In chemical manufacturing, intermediates must be reliable, selective, and efficient. 2-Chloro-4-(2,2-dimethylpropyl)pyridine fulfills these expectations due to:
- Predictable reactivity: The chloro group facilitates nucleophilic substitution, enabling downstream conversions.
- Stable structure: Its branched side chain contributes to thermal and chemical stability during reactions.
- High synthesis value: It serves as an essential foundation for producing more advanced specialty molecules.
- Scalability: Production runs can be scaled up without compromising product consistency, which is crucial for industrial buyers.
Because of these chemical characteristics, manufacturers rely on it when designing cost-efficient, high-yield reaction pathways.
Applications in Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pyridine derivatives are widely used in drug development, and this compound is no exception. 2-Chloro-4-(2,2-dimethylpropyl)pyridine serves as:
- A key building block for API intermediates where its chloro group enables substitution reactions to introduce functional groups essential for biological activity.
- A precursor in heterocyclic modification to fine-tune molecule solubility, metabolic behavior, or therapeutic potential.
- A reaction intermediate used to create compounds for anti-infective, anti-inflammatory, and metabolic disorder research (depending on the manufacturer’s formulation pipeline).
Its stable yet reactive profile makes it suitable for controlled pharmaceutical synthesis, where precision and purity are critical.
Uses in Agrochemical Production
Agrochemicals often rely on pyridine-based structures due to their effectiveness and tunable reactivity. This compound is frequently utilized in:
- Synthesis of pesticide intermediates, especially those requiring a pyridine ring as a core structural component.
- Development of herbicides or growth regulators where the compound helps build active molecules with targeted biological functions.
- Formulation optimization, thanks to its ability to undergo further modification to enhance efficacy, stability, or environmental compatibility.
Its consistent performance in chemical reactions helps agrochemical manufacturers maintain stable production quality while meeting regulatory and environmental standards.
Role in Specialty Chemical Synthesis
Beyond pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals, 2-Chloro-4-(2,2-dimethylpropyl)pyridine is valuable across multiple specialty chemical categories. It is used in:
- Fine chemical synthesis, especially where aromatic substitution or pyridine ring functionality is needed.
- Material science applications, such as producing tailored molecular additives and performance-enhancing compounds.
- Custom synthesis projects, including the development of proprietary intermediates for niche industrial applications.
Its adaptability allows chemists to incorporate it into unique reaction mechanisms, enabling the production of novel high-performance materials or functional chemicals.
Conclusion
2-Chloro-4-(2,2-dimethylpropyl)pyridine is a versatile and valuable intermediate widely applied in pharmaceutical research, agrochemical manufacturing, and specialty chemical synthesis. Its favorable reactivity, stability, and compatibility with multiple synthesis pathways make it a preferred choice for companies seeking reliable building blocks for advanced chemical products. As demand grows for more refined and efficient intermediates, this compound continues to play an important role in both large-scale industrial production and innovative chemical development.



