What is Benzoic acid, 3-bromo-2-fluoro-4-methyl-, methyl ester?
Benzoic acid, 3-bromo-2-fluoro-4-methyl-, methyl ester is an organic compound widely used as a chemical intermediate in pharmaceutical and fine chemical synthesis. It is a substituted benzoate ester, containing halogen atoms (bromine and fluorine) and a methyl group on the benzene ring, which make it a structurally versatile molecule.
Its CAS number is commonly listed as 1807043-92-0, and it is typically found as a colorless to pale yellow liquid or crystalline solid depending on purity and storage conditions. This compound’s halogenated aromatic structure provides useful reactivity for further functionalization in organic chemistry.
Chemical Structure and Molecular Properties
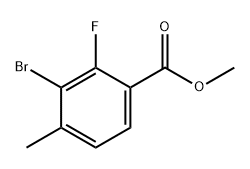
The molecular formula of Benzoic acid, 3-bromo-2-fluoro-4-methyl-, methyl ester is C9H8BrFO2, with a molecular weight of approximately 247.06 g/mol. It belongs to the benzoic acid ester family, in which the carboxylic acid group is esterified with methanol.
Key physicochemical properties include:
- Appearance: Colorless to pale yellow liquid or solid
- Boiling Point: Around 260–280°C (estimated, depending on pressure)
- Melting Point: Generally near room temperature (varies by purity)
- Solubility: Insoluble in water; soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol, ether, and chloroform
- Stability: Stable under normal temperature and pressure; sensitive to strong oxidizers
The combination of bromine and fluorine atoms contributes to the compound’s enhanced chemical stability and electrophilic reactivity, making it valuable for use in synthetic chemistry.
Applications and Uses
This compound is primarily utilized as an intermediate in organic synthesis. Its halogenated and methyl-substituted aromatic ring allows for selective substitution or coupling reactions, which are essential in the production of more complex molecules.
Common applications include:
- Pharmaceutical intermediates: Used in the synthesis of potential bioactive molecules, drug candidates, and aromatic building blocks.
- Agrochemical synthesis: Serves as a precursor in developing new pesticides and herbicides.
- Fine chemicals and materials: Applied in the preparation of specialty aromatic compounds used in coatings, resins, and advanced materials.
Researchers also use this ester in structure–activity relationship (SAR) studies, due to its reactive halogen sites that can be easily modified to explore new chemical derivatives.
Storage and Transportation Guidelines
To maintain product quality and ensure safety, Benzoic acid, 3-bromo-2-fluoro-4-methyl-, methyl ester should be stored and handled carefully:
- Storage Conditions: Keep in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area. Avoid direct sunlight and heat sources.
- Container Requirements: Store in tightly sealed containers made of glass or compatible plastic materials.
- Handling Precautions: Use gloves, goggles, and appropriate protective clothing. Handle in a fume hood to prevent inhalation of vapors.
- Transportation: Classified as a non-hazardous chemical for transport under most regulations, but it should be kept upright and securely closed during shipment.
If spilled, absorb the material with an inert substance (such as vermiculite) and dispose of it following local environmental regulations.
Summary
Benzoic acid, 3-bromo-2-fluoro-4-methyl-, methyl ester is a versatile aromatic ester recognized for its halogenated and methylated structure. Its distinctive molecular features make it a valuable intermediate for pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and fine chemical industries. With proper handling and storage, it remains stable and effective for a variety of laboratory and industrial synthesis applications.



