Key Properties and Uses of 1-Bromo-4-(tert-butyl)-2-methylbenzene
Oct 28, 2025
ChemPacific
What is 1-Bromo-4-(tert-butyl)-2-methylbenzene?
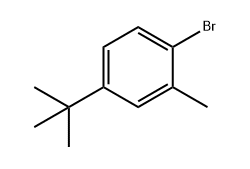
- Chemical Identity: 1-Bromo-4-(tert-butyl)-2-methylbenzene is an aromatic bromide with a benzene ring substituted with a bromine atom, a tert-butyl group, and a methyl group.
- Molecular Formula and Weight: Its formula is C11H15Br and molecular weight is 203.14 g/mol.
- Physical Form: Usually supplied as a colorless to pale yellow liquid at room temperature.
- Chemical Behavior: The bromine atom provides reactive sites for substitution reactions, while the tert-butyl and methyl groups offer steric protection, making it suitable for selective organic synthesis.
- Usage Context: Commonly used as an intermediate in pharmaceutical, agrochemical, and specialty chemical manufacturing, as well as research laboratories for organic synthesis.
Which Physical Properties Should You Know?
- Appearance and Density: Colorless to pale yellow liquid; density approximately 1.14 g/cm³ at 20°C.
- Melting and Boiling Points: Melting point around -60°C; boiling point approximately 219–221°C, which allows liquid handling under standard laboratory conditions.
- Solubility: Insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents like ethanol, acetone, and ether, making it versatile for different reaction media.
- Vapor Pressure and Stability: Low vapor pressure at room temperature, reducing evaporation risks; chemically stable under normal storage conditions.
- Implications for Handling: Knowledge of these properties helps buyers choose appropriate storage, reaction solvents, and safety measures.
Where is this Chemical Commonly Used?
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Used in the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), especially where selective bromination or aryl substitution is required.
- Agrochemical Applications: Acts as a building block for herbicides, insecticides, and fungicides, enabling creation of molecules with targeted biological activity.
- Organic Synthesis: Suitable for cross-coupling reactions such as Suzuki and Heck reactions to produce complex aromatic compounds for dyes, pigments, and specialty chemicals.
- Research and Development: Employed in laboratories for designing novel compounds due to its predictable reactivity and stability.
- Industrial Relevance: Its versatility allows both small-scale research use and large-scale industrial production.
How Should You Handle and Store it Safely?
- Storage Conditions: Keep in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area, away from heat, sparks, and open flames; store in tightly sealed containers made of compatible materials like glass or HDPE.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Gloves, goggles, lab coats, and possibly respirators when handling larger quantities or in poorly ventilated areas.
- Handling Practices: Avoid inhalation, ingestion, and skin contact; always handle with care to prevent spills.
- Spill and Disposal Measures: Use inert absorbent materials for spills, collect properly, and dispose according to local environmental regulations.
- Fire Safety: Flammable under certain conditions; suitable chemical fire extinguishers should be accessible.
- Compliance: Following these guidelines ensures safety, maintains product integrity, and aligns with occupational health standards.
Why Purity and Quality Matter for Ur Purchase?
- Impact on Reaction Yields: Impurities can reduce yield, produce unwanted by-products, and complicate downstream purification.
- Regulatory Requirements: High-purity products are essential in pharmaceutical and agrochemical applications to meet safety and compliance standards.
- Laboratory vs. Industrial Use: Laboratory-grade chemicals may allow slightly lower purity, but industrial or commercial applications require consistently high quality.
- Verification Methods: Buyers should request Certificates of Analysis (CoA) and batch test results to confirm purity, moisture content, and other critical parameters.
- Cost and Efficiency Benefits: High-quality products improve reaction efficiency, reduce waste, and lower overall production costs.
- Supplier Selection: Choosing reliable suppliers ensures consistent quality across multiple batches, minimizing operational risks.




